In my last post, I showed you how process modelling works by visualizing cooking recipes.
Of course, I haven´t modelled straight on, but I had to follow some "basic rules of EPC modelling".
Therefore, I show you today which basic rules exist.
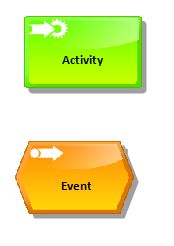
An Activity (or Function) describes an incidental task that typically consumes time and resources. Therefore, it is an active component and has decision-making authority.
An Event describes, in accordance with DIN 69900, an occurred defined condition that causes a sequence of activities. Therefore the event is a passive component and may have no function in contrast to the decision-making authority. Events can trigger functions. Functions are triggered by events. Events describe an occurring condition.
Short overview of Rules
Generally, you start with an Event, if you model an EPC.
A number of Activities can follow an Event. In the past, it was said, that Events and Activities must alternate. This leads to very long process models with a lot of trivia events. Therefore, we suggest today to only add an event, if an important state change needs to be documented.
Recommendation, when using Events:
- at the beginning of the process or after start-process interfaces
- at the end of the process or before the end of process interfaces
- Decision events by XOR or OR connectors
- for important events, for example Milestones in project
Activities or Events must not have more than one outgoing or incoming Connection.
The control flow of the process is modelled using Rules (gateways).See afterwards, which Rules exist.
Rules can be used as follows:
- Of exactly one ingoing Connection follow a number of outgoing Connections (SPLIT).
- Of a number of ingoing Connections follow exactly one outgoing Connection (JOIN)
A sequence of Rules is possible.
An EPC is generally closed with the same operator like it was opened.
You end the EPC with an Event.
Logical operators
In an EPC you can use following Rules:
SPLIT: The processing steps that follow the rule occur in parallel and have to be performed.
JOIN: All processing steps for incoming connections must be completed so that the processing steps that follow the rule can be performed.
SPLIT: Exactly one of the following rule processing steps must be executed.
JOIN: Only one of the processing steps for incoming connections may be completed so that the processing steps that follow the rule can be performed.
SPLIT: At least one of the following rule processing steps (or even several or all processing steps) must be performed.
JOIN: At least one processing step (or even several or all processing steps) must be completed, whereupon the processing steps that follow the rule can be performed.
For logic operations between Events and Activities, there are special rules, which are shown in the ARIS Express model attached to this post. For your convenience, I also added a screenshot of the rules below:
I put this summary of the rules next to my monitor while modelling. It helps me a lot. I hope it helps you, too! So long, have fun modelling till my next post.


.jpg)
.jpg)




Mitesh Kumar on
Thanks Ramona. That was insightful as I am new to ARIS and BPM.
What are the rules applicable for connectors- where do they converge to & diverge from typically